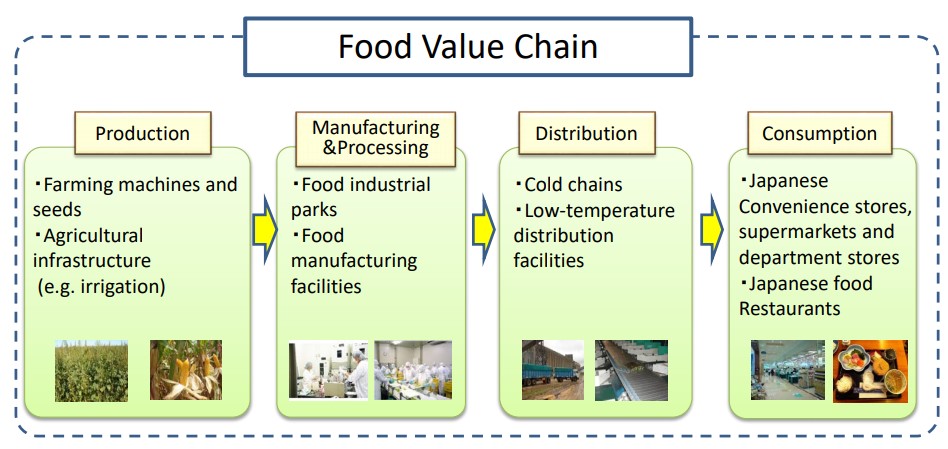
Food Value Chain フードバリューチェーン
WORK’IN JAPAN
25.09.2020
Food Value Chain
フードバリューチェーン
This is our first article in this series about food value chain in Japan. The Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries has an extensive program to add value to the food value chain throughout Asia.
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries
In these four articles, we will explain the Food Value Chain process; everything from agriculture and production to how products end up ready for consumers. There are many opportunities for collaboration between Japan and South East Asian countries when it comes to food production and contributing to a robust food value chain in Japan.

The world of agriculture is changing dramatically for the first time in centuries. The introduction of new farming technology through AI and IoT development is driving governments and farmers to approach agriculture differently. With a greater understanding of how farming practices impacts the planet, this is a golden opportunity to improve humanity’s relationship with the earth and how we consume agriculture products.
There are several benefits to ASEAN countries partnering with Japan to create Food Value Chains. First, it promotes the active trade of new agricultural technologies to other countries. ASEAN and East Asian countries are in the unique position through location, current state of the economy, and the ever-developing landscape of agriculture tools.

In production, let’s first examine one example of small farmers.
Small famers have an advantage in restructuring the food value chain. By having more product flexibility and a larger opportunity for biodiversity, small farmers can maximize their products and profits. Partnerships between farmers, as well as local governments and the private sector, can help farmers reach new profit highs.
The one important aspect of these ventures is that they be sustainable and scalable. These developments are meant to benefit all aspects of crop-related industries, from farming, to manufacturing, to retail and education.
In Japan, many universities and companies are working on technologies like robots to improve the success of sustainability and scalability of agriculture. In a previous article, we explained some of the robots that are being used in Japan to reduce the burden of physical labor for aging farmers. These developments are also an integral part of the future of farming.